1.3 Computer Hardware Review
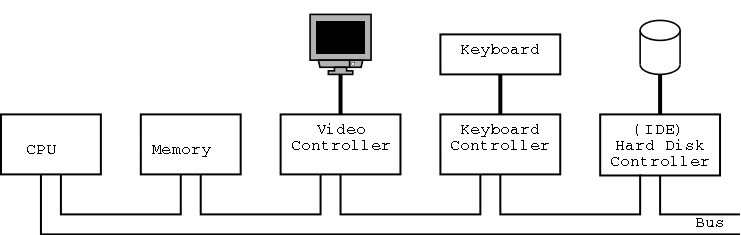
- The picture above is very simplified; it represents a 1980 design. (For one thing, today separate buses are used to Memory and Video.)
- A bus is a set of wires that connect two or more devices.
- Only one message can be on the bus at a time. All the devices receive the message: There are no switches in between to steer the message to the desired destination, but often some of the wires form an address that indicates which devices should actually process the message.
1.3.1 Processors
- Many of these issues are mentioned in 201 and nearly all of them are covered in 436, the computer architecture elective.
- We do, however, need the notion of a trap, which is an instruction that atomically switches the processor into privileged mode and jumps to a pre-defined physical address.
Multithreaded and Multicore Chips
Many of the OS issues introduced by multi-processors of any flavor are also found in a uni-processor, multi-programmed system. In particular, successfully handling the concurrency offered by the second class of systems, goes a long way toward preparing for the first class. The remaining multi-processor issues are not covered in this course
1.3.2 Memory
<aside>
💡 The central memory in a system is called RAM (Random Access Memory). A key point is that RAM is volatile, i.e. the memory loses its data if power is turned off. Hence when power is turned back on, the RAM contains junk. Thus the first instructions executed at power-on cannot come from RAM.
</aside>
ROM / PROM / EPROM / EEPROM / Flash Ram
- ROM (Read Only Memory) is used for (low-level control) software that often comes with devices on general purpose computers, and for the entire software system on non-user-programmable devices such as microwaves and dumb wristwatches. It is also used for non-changing data.
- But often this unchangable data needs to be changed (e.g., to fix bugs). This gives rise first to PROM (Programmable ROM), which, like a CD-R, can be written once (as opposed to being mass produced already written like a CD-ROM), and then to EPROM (Erasable PROM), which is like a CD-RW. Early EPROMs needed UV light for erasure; EEPROM, Electrically EPROM or Flash RAM) can be erased by normal circuitry, which is much more convenient.
1.3.6 Buses
On the right is a figure showing the specifications for an Intel chip set introduced in 2000. The terminology used is not standardized
<aside>
💡 As shown this chip set has two different width PCI buses. This particular chip set supplies USB. An alternative is to have a PCI USB controller.
</aside>



